The Organizational structure guide is the basic framework for setting up a company, in which actions are performed in relation to organizations, departments, positions and employees.
The organizational structure is represented as a hierarchical tree and contains the following nodes:
-
Organization is the top level of an organizational structure, usually corresponding to an enterprise (legal entity)
-
Department is an element of an organizational structure within which positions are created.
Departments can have a hierarchy of any complexity.
-
Position is the subject of all communications within the company and with external counetrparties.
-
Employee - receives an appointment to a position and thus access to all information of the position and the ability to perform actions on behalf of the position.
Read more about the meaning of the terms company, position, employee and appointment in this article.
The rights to configure the organizational structure, namely to create and modify any of its elements, are granted to an employee with the role of Owner, Administrator, or a custom role with the appropriate permissions.
The directory interface consists of a left pane of the hierarchical structure (Organisation > Department > Position > Employee) and a right pane that displays all information about the element of the structure that is in focus.
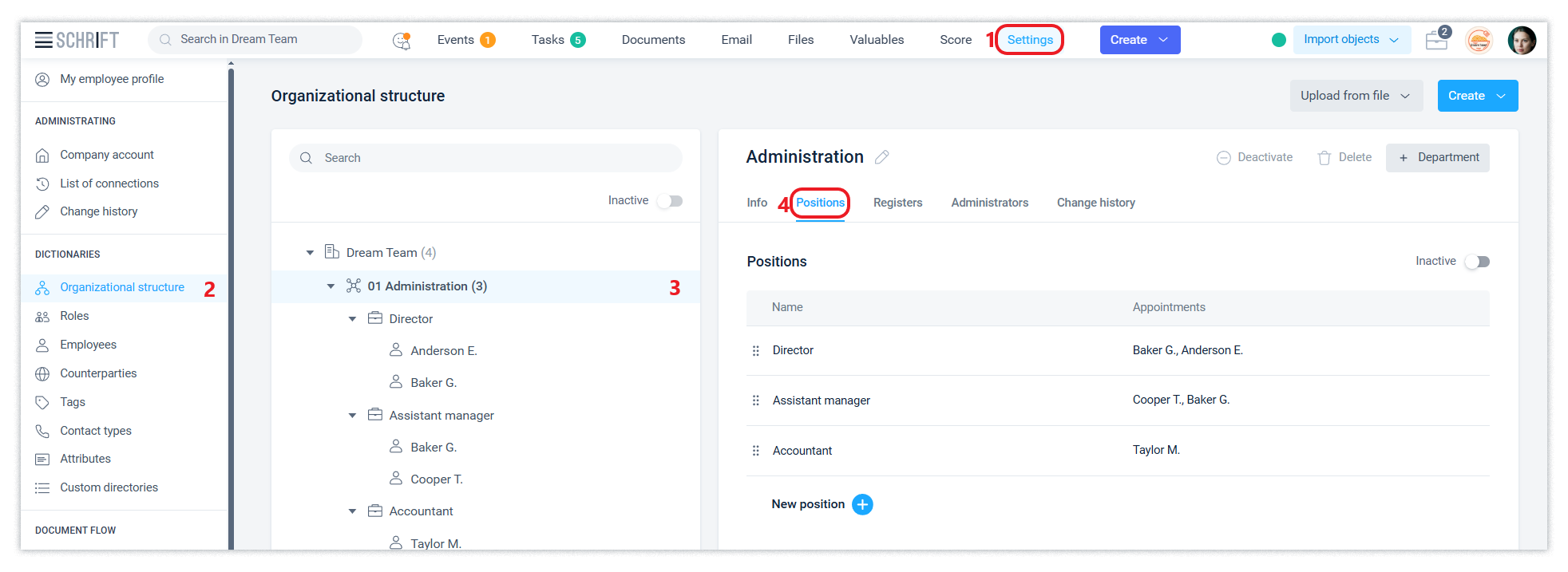
You can change the name of the organisation, department and position at any time. The system saves all records of settings changes in the Change history tab of the corresponding structure element.
The event information supports the display of Historical information, i.e. information about the positions and appointments at the time of the event creation, if this information differs from the current one.
Importing data from an excel file
Organisational structure data can be imported using an Excel file. To do this, you need to download a template, fill it in and upload the data to the system.
This service can be useful if the company has a lot of data to configure and it is more convenient for the company administrator to prepare this data in a file.

When re-importing data from a file, the Schrift system does not duplicate previously loaded data if the foreign key fields (the 1st field on each page of the file) were used in this data.
Organization
Within an organization, a structure (hierarchy) of departments is created. A company can have many organizations, each of which will have its own departmental structure.
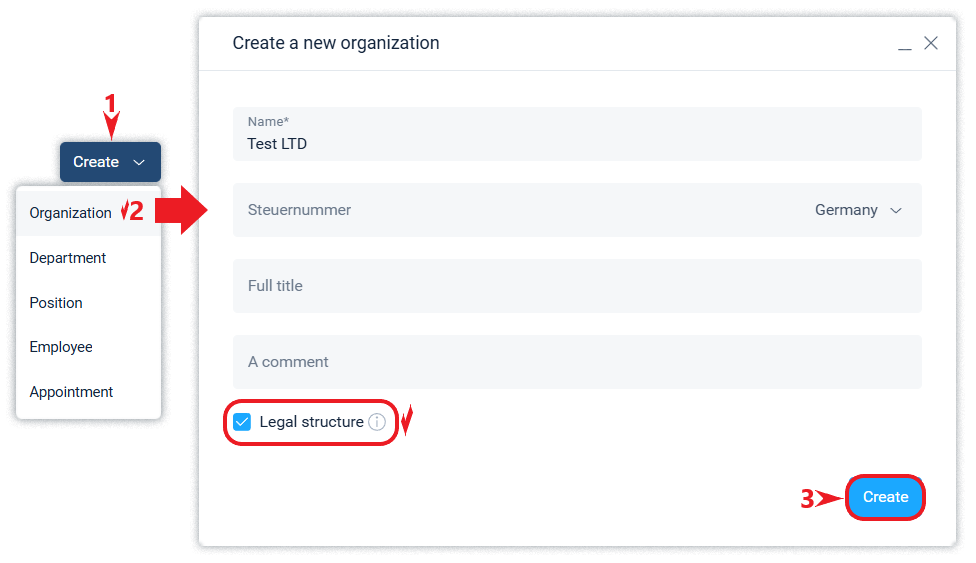
Creation of the organisation
You can create a new organisation in the company using the Create button.
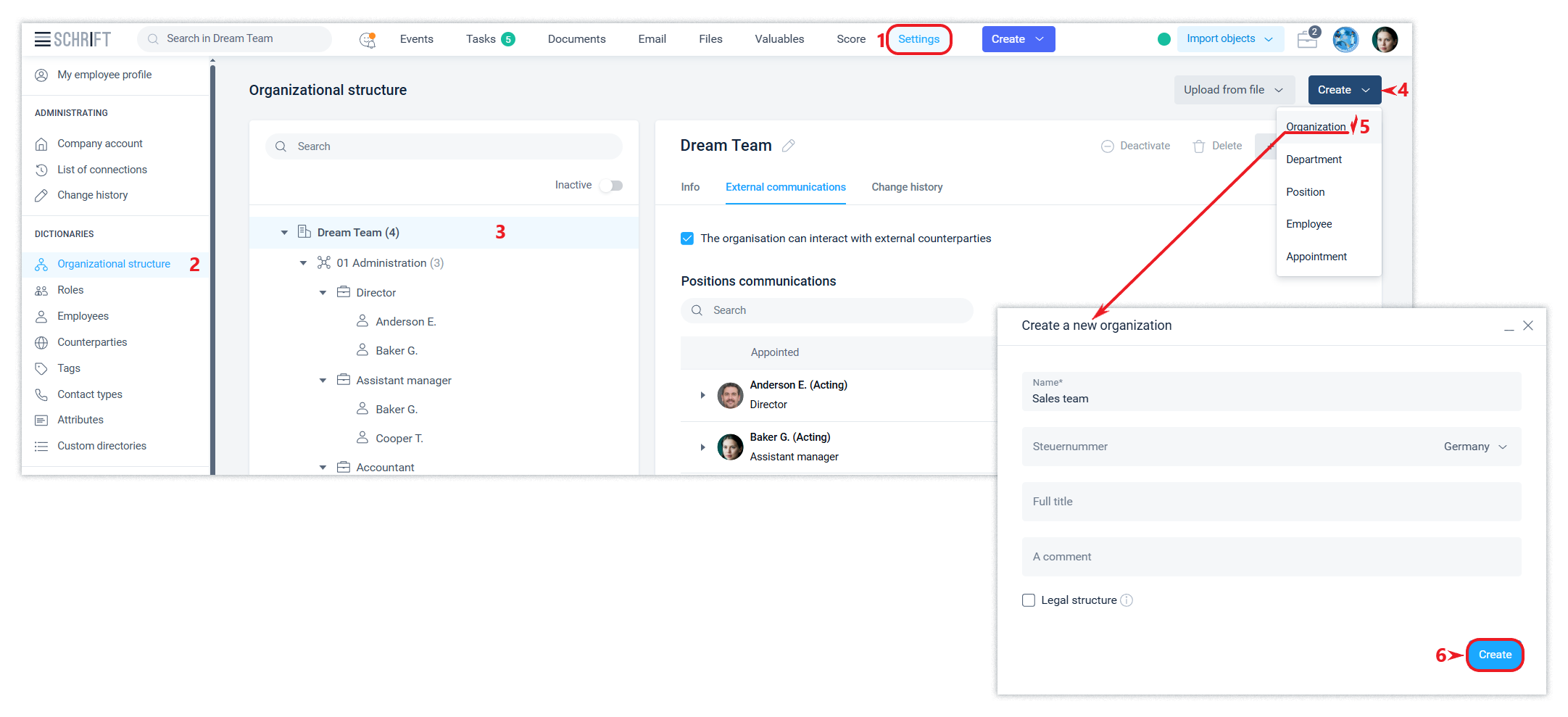
The creation of the 2nd and subsequent organizations is available at paid tariffs.
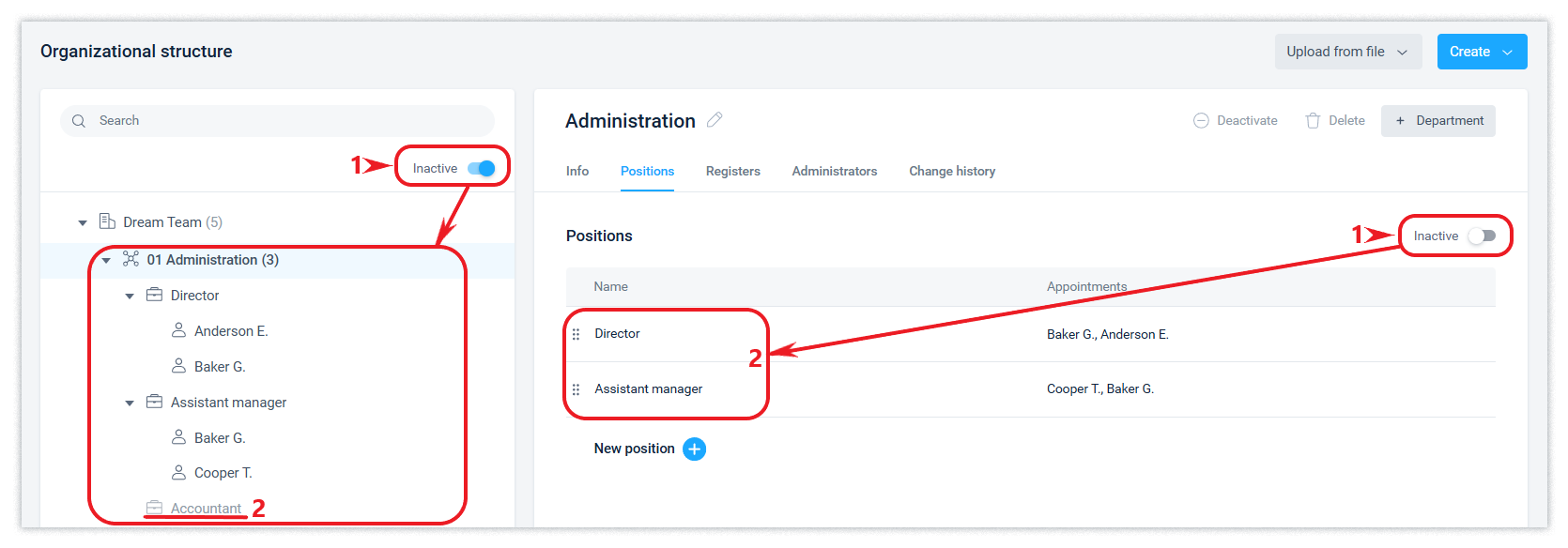
An organization can be deleted if it has no departments. This logic works for any node in the organizational structure and company directories and ensures that data integrity is maintained. If an item cannot be deleted, it can be deactivated, provided that its subordinate items have been previously deleted or deactivated.
Deactivated nodes of the structure will be hidden from the list. You can view them and, if necessary, activate them by enabling the Inactive filter.
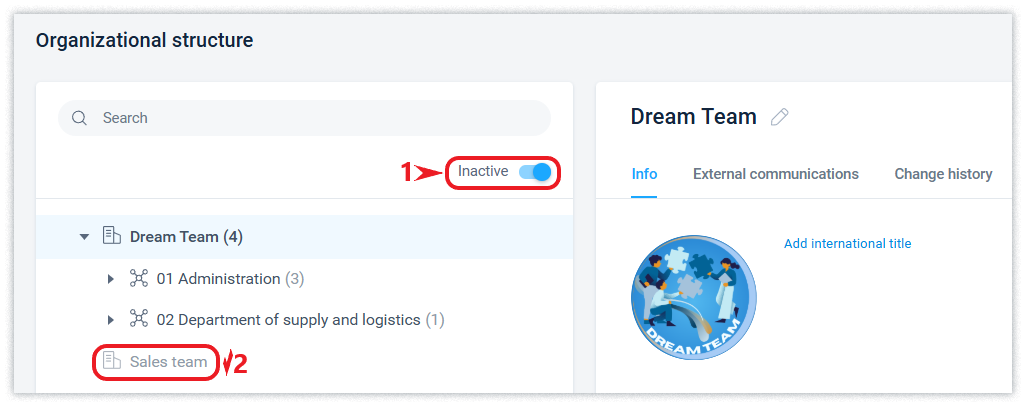
In the External communications tab, the row of the corresponding organization enables or disables the organization's ability to communicate with counterparties, which is described in more detail in this article.
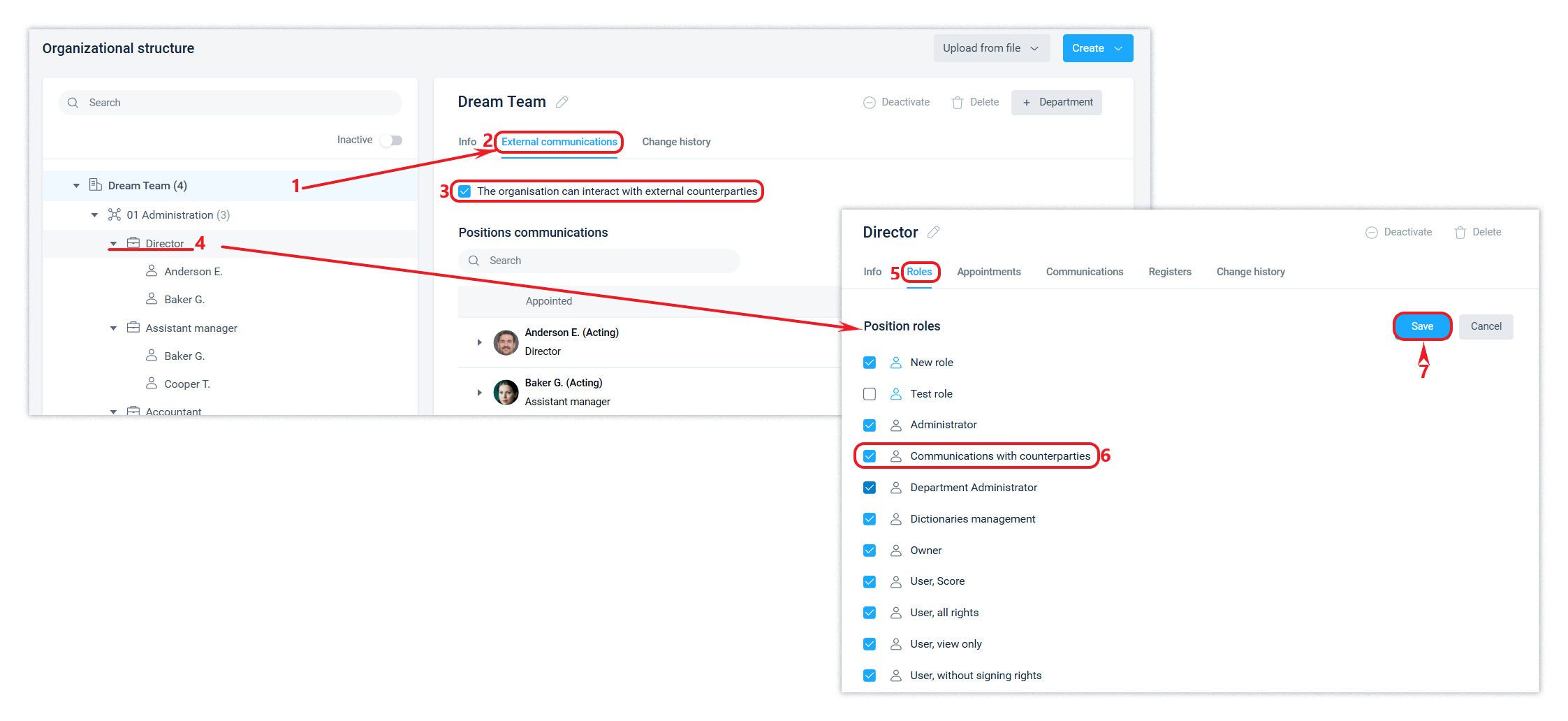
For organisations, you can enable hiding of their name and position titles in this organisation from external contacts. This feature is described in more detail in this article.
Legal structure
The Schrift system supports the creation of organizations with the “Legal structure” attribute. The purpose of creating such an organization is to create a link between a position in the functional structure and its ‘mirror’ in the legal structure. As a result, external contacts will see information about such a position (for them, it is also an external contact) in the part of the organization name and position as they are indicated in the legal structure.
This option will be useful for a company where the functional organizational structure differs from the legal structure, and the functional structure should not be accessible to external contacts.
The first organization that is created in a new company is the functional structure. The functional structure contains all the details of the setup.
Organizations with the Legal structure attribute have limited configuration options. In such organizations, you can create departments and positions, but you cannot create registers, appoint employees to positions, or configure roles and communication rules for positions. In other words, the main purpose of customization is to create a link between a position from the functional structure and a position from the legal structure.
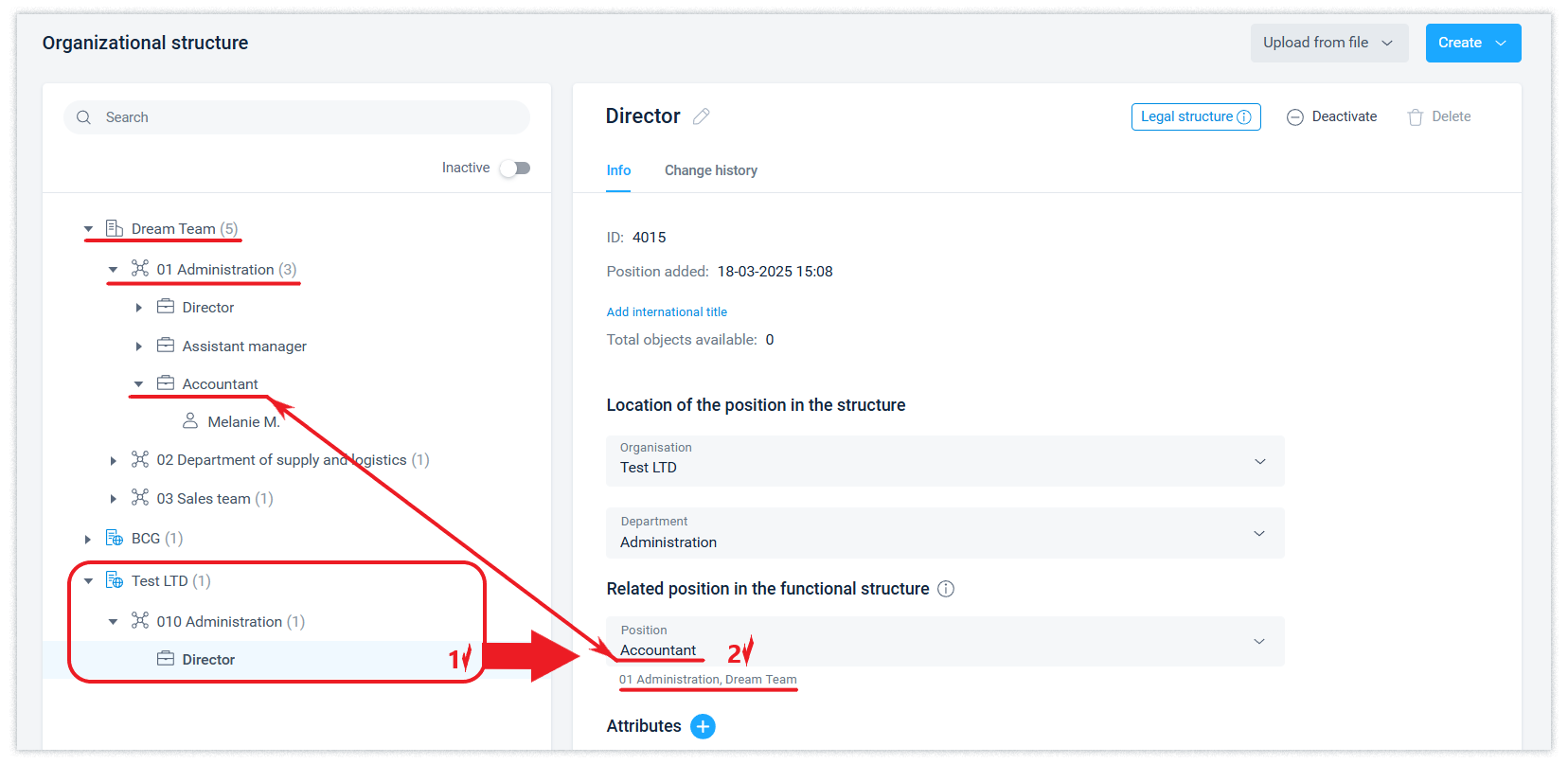
For a legal structure organization, the external communication right is enabled by default. Once a position in the functional structure is linked to its mirror in the legal structure, the external communication right will be determined by the availability of this right in the legal structure organization and the External Communications role of the corresponding position in the functional structure.
After setting up the linkage of a position from the functional structure to the legal structure, the position pop-up window in the company interface will additionally display information about the name of the organization and the position by legal structure.
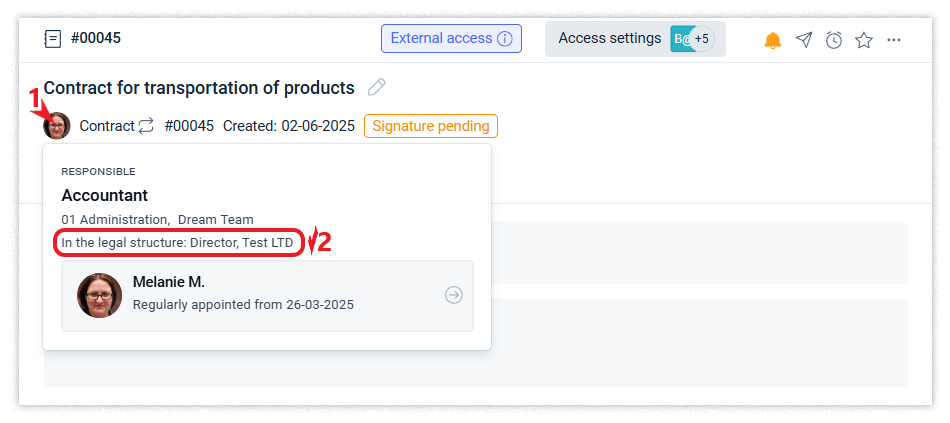
The information specified in the QR code of the registered document contains information about the name of the organization of the signatory specified in the QR code, based on the legal structure, if the signatory position has a ‘mirror’ in the legal structure.
Departments
You can create a new department by clicking the Create directory button or from an organization by clicking the +Department button.
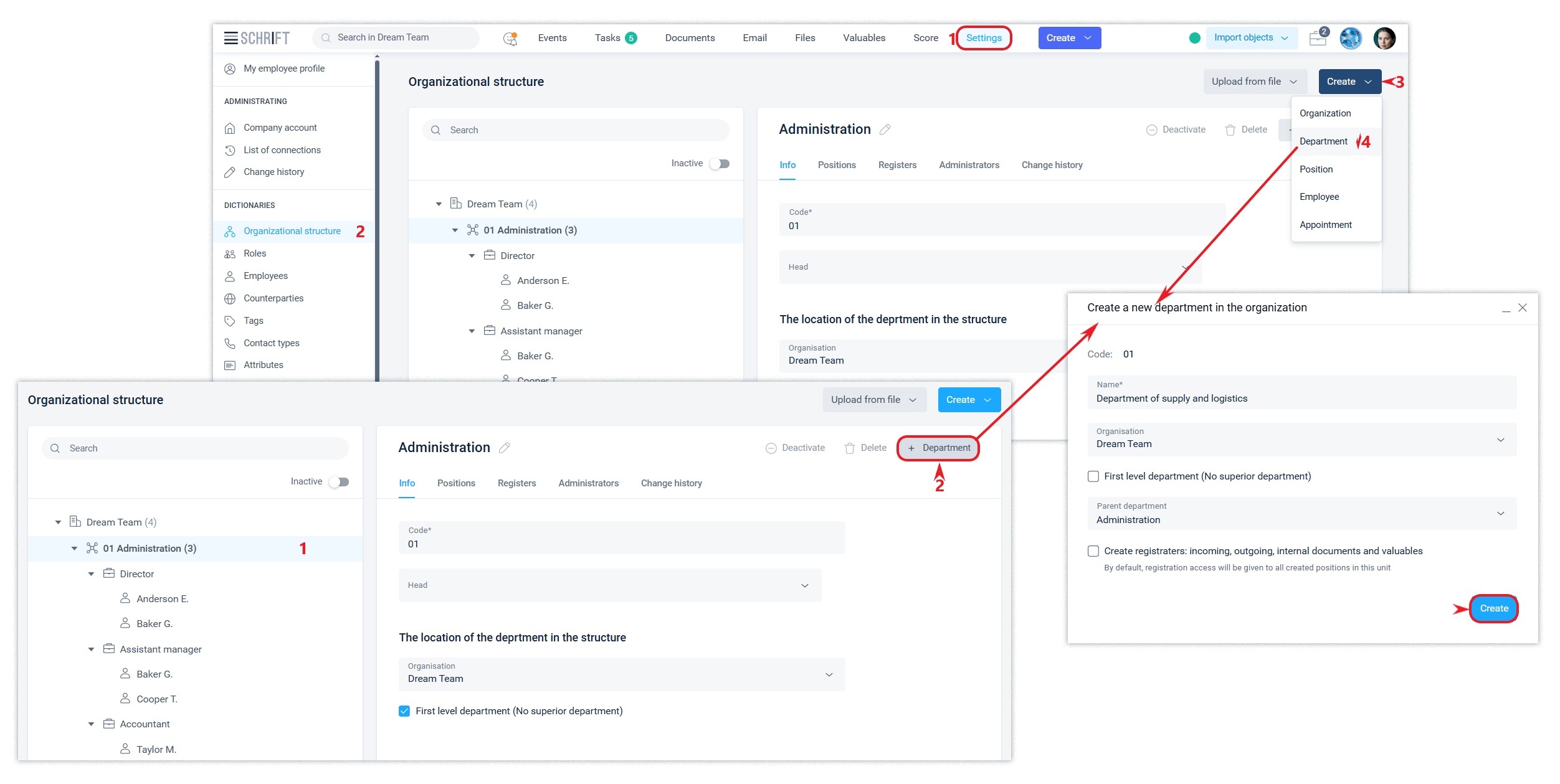
The code (digital identifier) of the department is generated automatically and is presented in the order of the digital description of the structure.
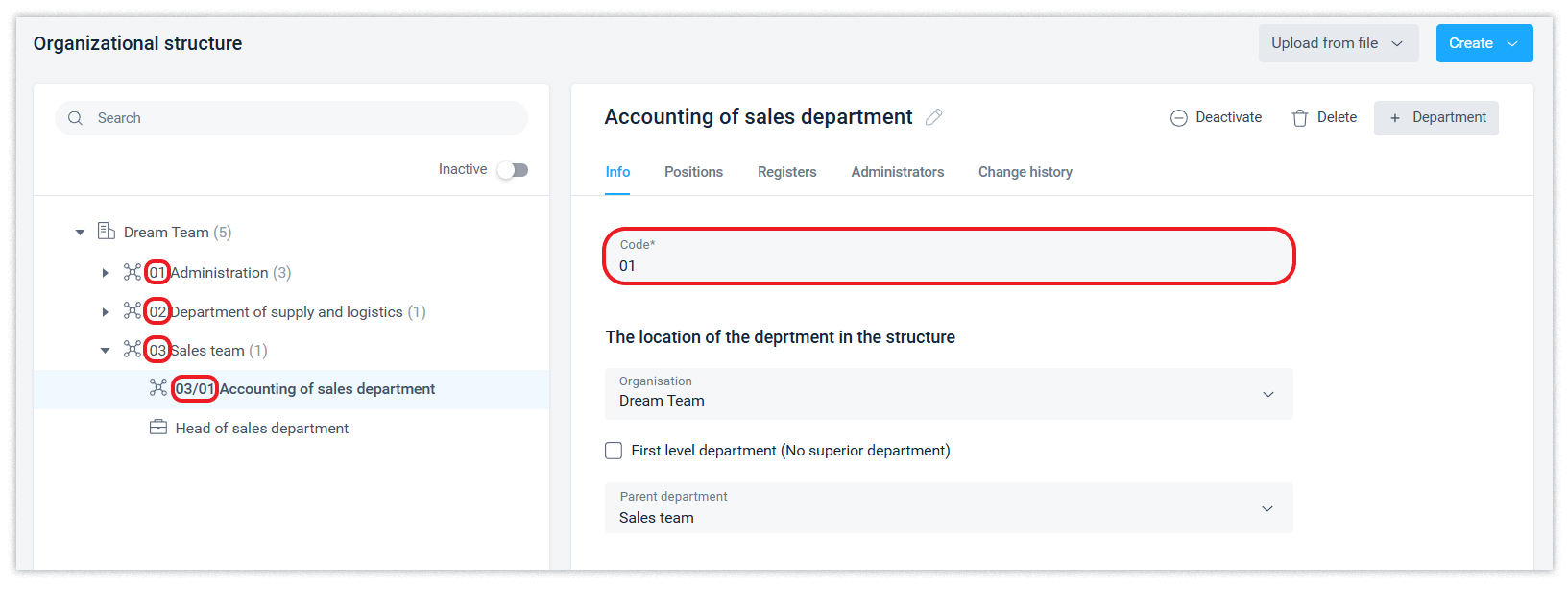
When creating a department, you need to specify its name, select the organization in which the department will be created if there is more than one organization, and specify at what level of the hierarchy it will be. If necessary, select a First level department from the list, and determine whether you want to create a separate set of registers for this department.
If a separate set of registers is not created for a department, the administrator will need to configure access to the registers that exist in other departments for the positions of this department.
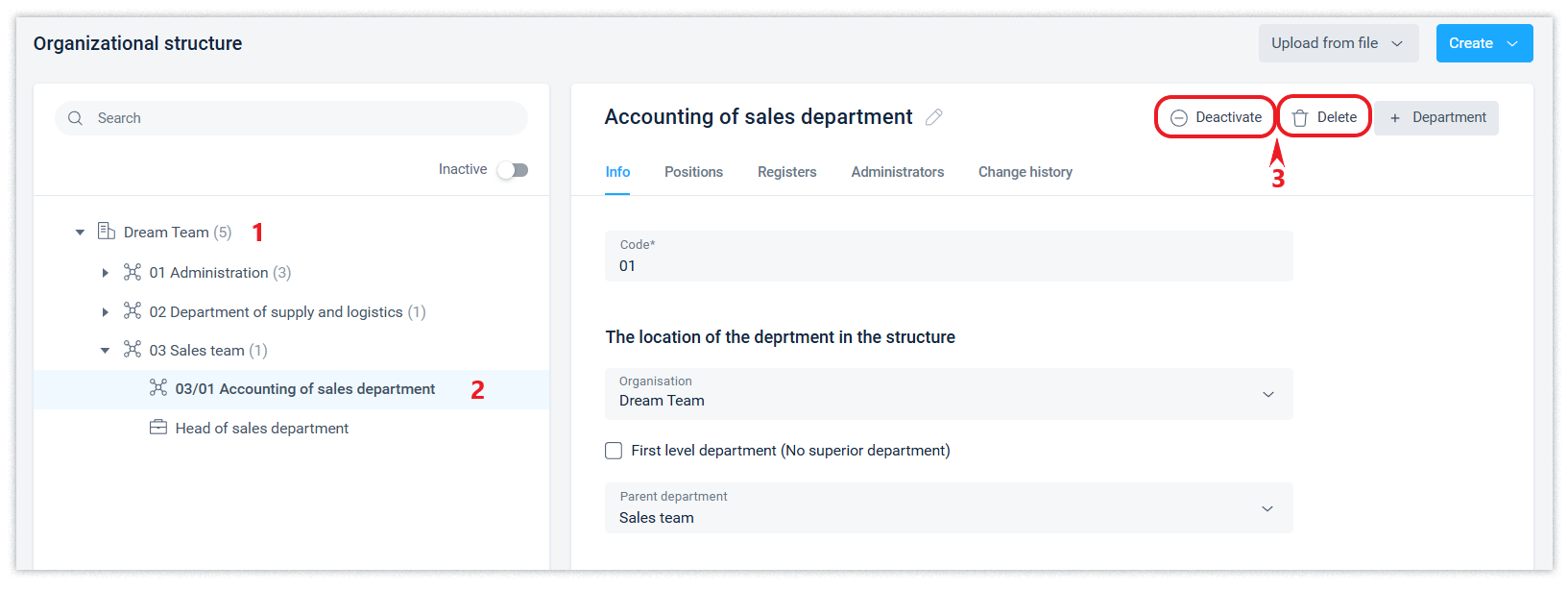
Departments can be deleted or deactivated using the corresponding buttons in the department interface with the same restrictions as described in the last paragraph of this article.
A department can be moved to another organization or another department. All departments and positions within the department will be moved with the department.
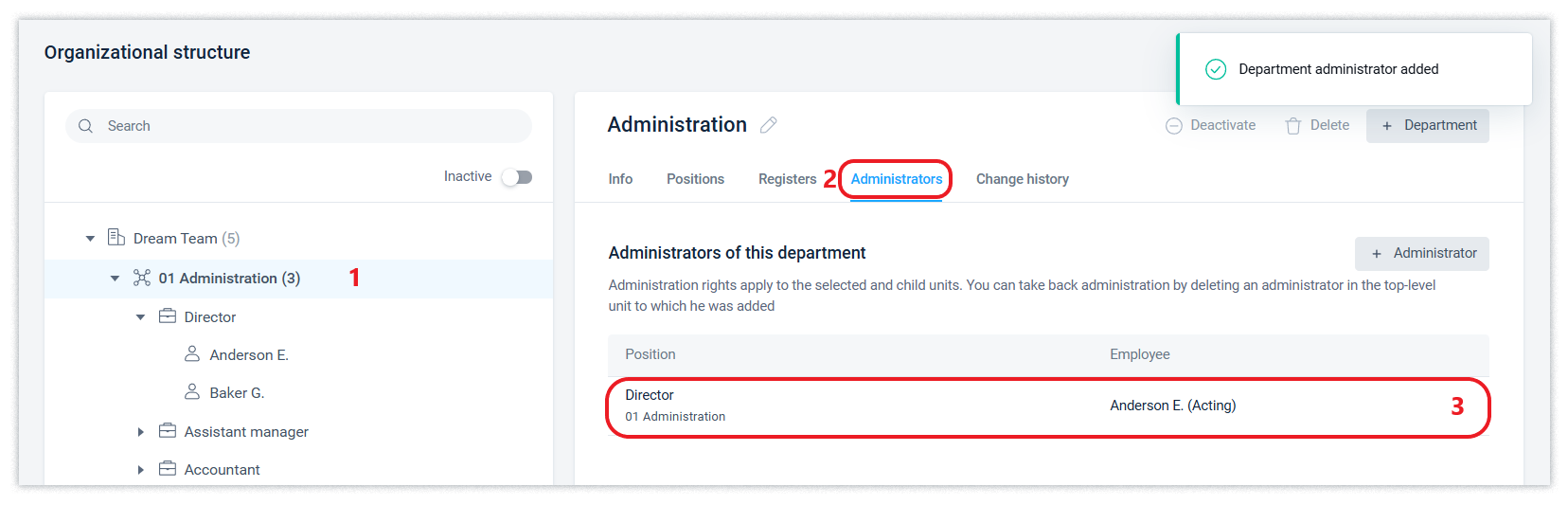
For separate administration of department, you can designate a position as a department administrator and assign a corresponding role. This makes it possible to limit the rights of such an administrator to this department, its subordinate departments (included in its structure) and positions in them, and employees appointed to these positions.
Positions
You can create a new position by clicking the Create button of the Organizational structure directory or from the department line of the structure tree, in the Positions tab, click the New position + button.
Appointment to a position and inviting an employee to the company is described in this article.
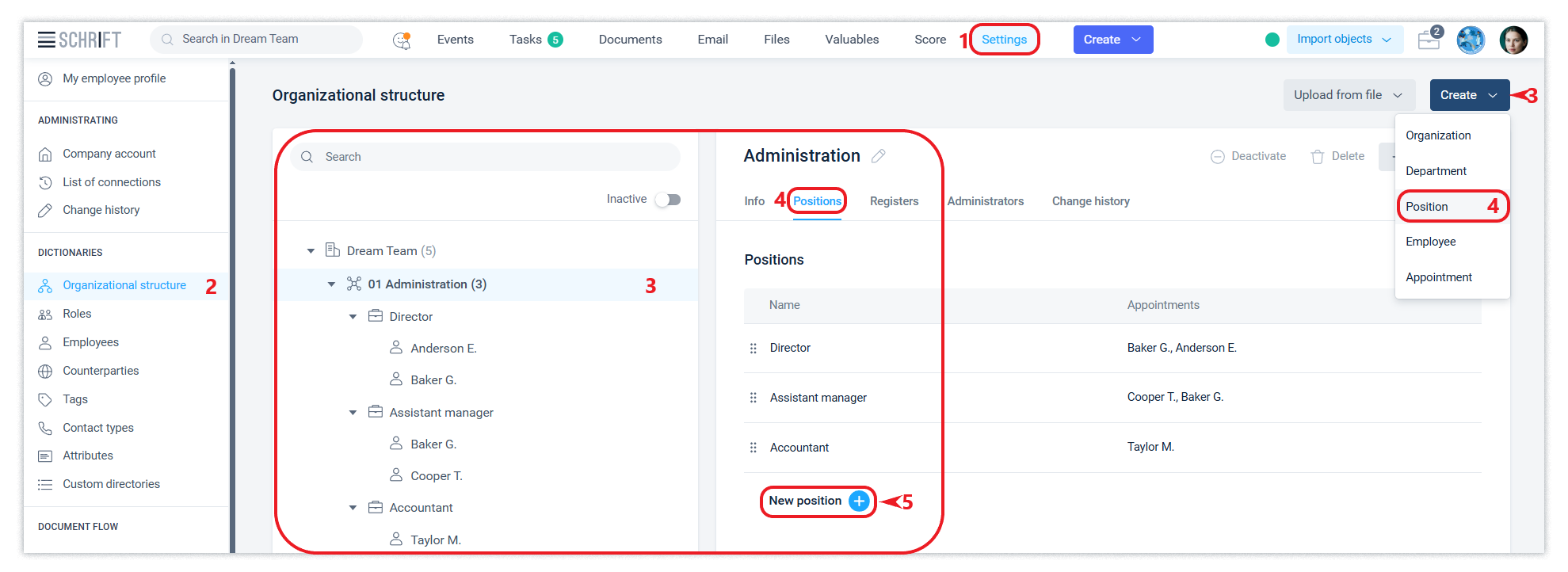
Since all employee actions in the system with system objects (documents, etc.) are performed on behalf of a position, an employee who is appointed to a certain position thus gains access to the information available to that position.
This makes it possible to instantly provide access to all the information available to the position when a new employee is appointed.
The system supports 3 types of appointment: regular appointment, acting appointment and assistant appointment. One position at any given time can have only 1 regular, 1 acting, and an unlimited number of assistants.
The position can be moved to another unit. Moving a position will not affect the existing appointments for that position.
The system stores and displays essential information about the position, i.e. the status of the appointment at the time of the relevant event in which the position was involved. Read more about this in the relevant article.
Selecting positions
One employee can be appointed to several positions. The employee will see a list of available positions in the main menu and will be able to select the positions on behalf of which he/she are currently working in the system.
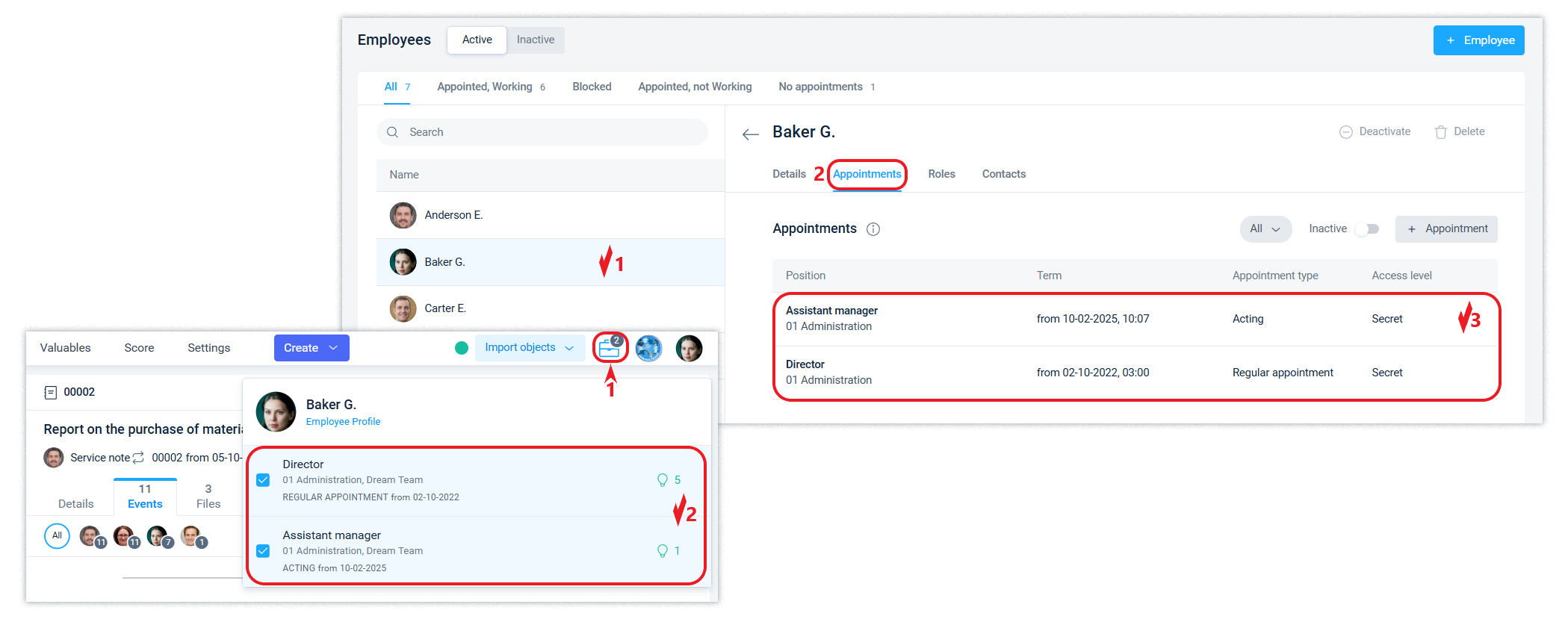
Employees can independently delegate their powers by appointing assistants and acting in the employee profile.
Vacant and liquidated positions
A vacant position (that has no active appointments) cannot communicate with other positions because there is no employee who can perform actions on behalf of that position.
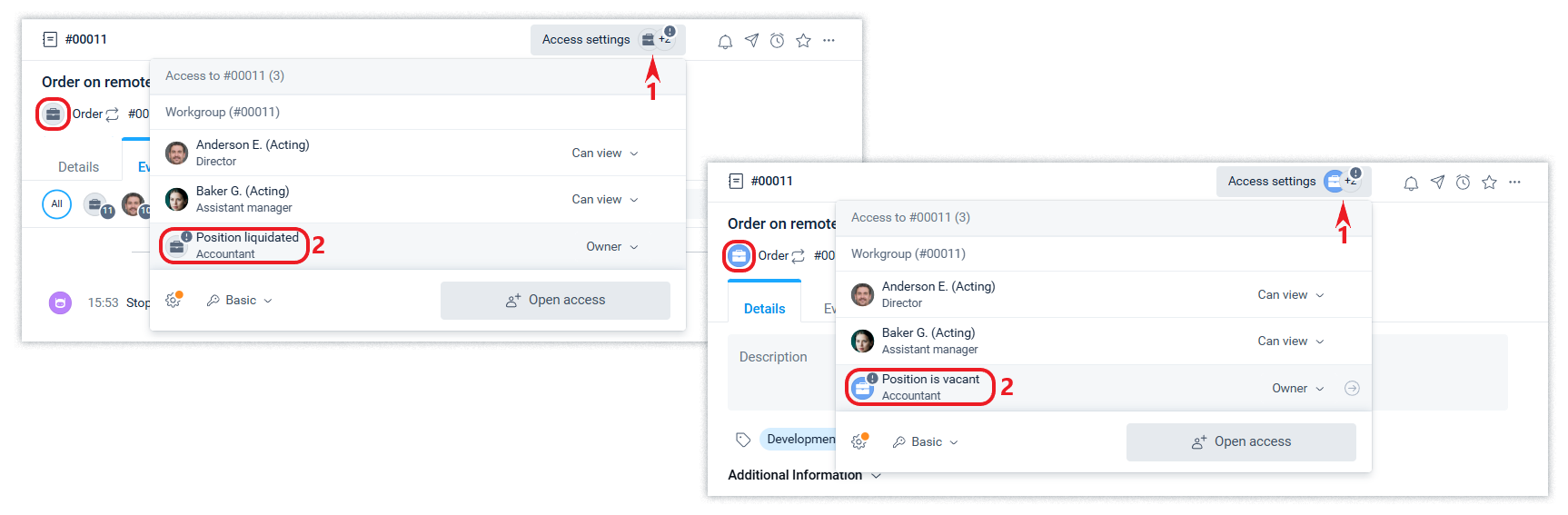
A position can be deleted or deactivated (liquidated) by corresponding actions in the interface, with the same restrictions as described in the last paragraph of this article.
You can reactivate a position (return it to active) and make new appointments to it. In this case, its settings (rights to communication, work with registers, and other actions) that were valid at the time of deactivation will be applied.
If the position that has become vacant is not planned to be used in the future, it should be liquidated. Regardless of whether another employee is to be appointed to the position, the documents available to the position can be transferred to another position (all or partially), left as is, or the position can be denied access to all documents that were available to it. The choice of option depends on the specific circumstances and the company's corporate culture.
If only an assistant has an appointment for a position, the position remains vacant. The actions of the assistant for such a position will be limited to viewing data only, since there is no employee associated with this position. An employee associated with a position can only be a regularly appointed employee or an acting.
Setting up communication rules between positions
To manually configure the appropriate communication rights between positions when the “Unlimited” mode of information exchange and task assignment is turned off, use the Communications tab from the line of each position to be configured.
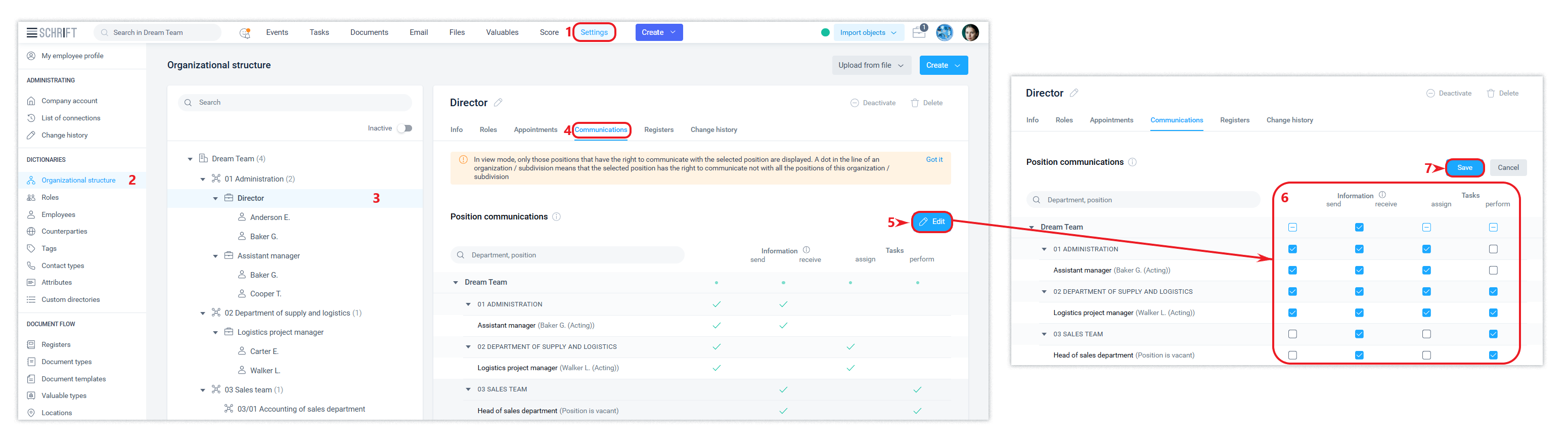
If your company has enabled manual configuration of communication permissions between positions, please note that at the time of creation, a position automatically receives the right to communicate with other positions only in the department in which it is created.
International names
If your company's employees or counterparties use different language settings, the Schrift system offers the option of adding international names to the organization name, position, and employee name.
To do this, just add such international names in Latin and they will be displayed instead of the main names for those for whom it corresponds to their language settings.
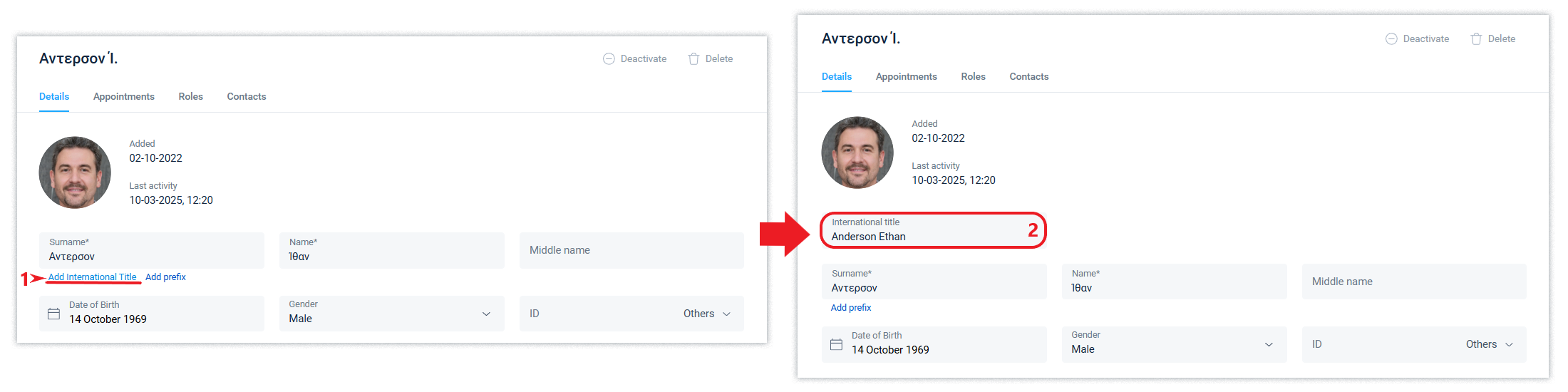
The corresponding additional fields are present in the above system entities.
Within your company, the corresponding international name is displayed: for the employee's first and last name, by comparing it to a country of he/she properties, and for the organization name and position, by comparison with a country of the organisation's properties. If they match, the employee's name, organization name, and position are displayed in their basic spelling, and if they do not match, their international names are displayed, if they have been set.
Read about the use of international names in external communications in this article.
Transferring documents and closing/opening access
An employee with the role of owner, administrator, or department administrator can perform actions to transfer system objects (documents, etc.) from one position to another, as well as close and open access to them.
There are 3 options for changing access: transferring objects to another position, closing access, and opening access. During the transfer, access to the object is opened to the target position and closed to the original one. When closing access, the target position is not needed, since as a result, the access of the original position will be closed. When opening access, the target position is granted access only to the object or to all events for it that are available to the source position.
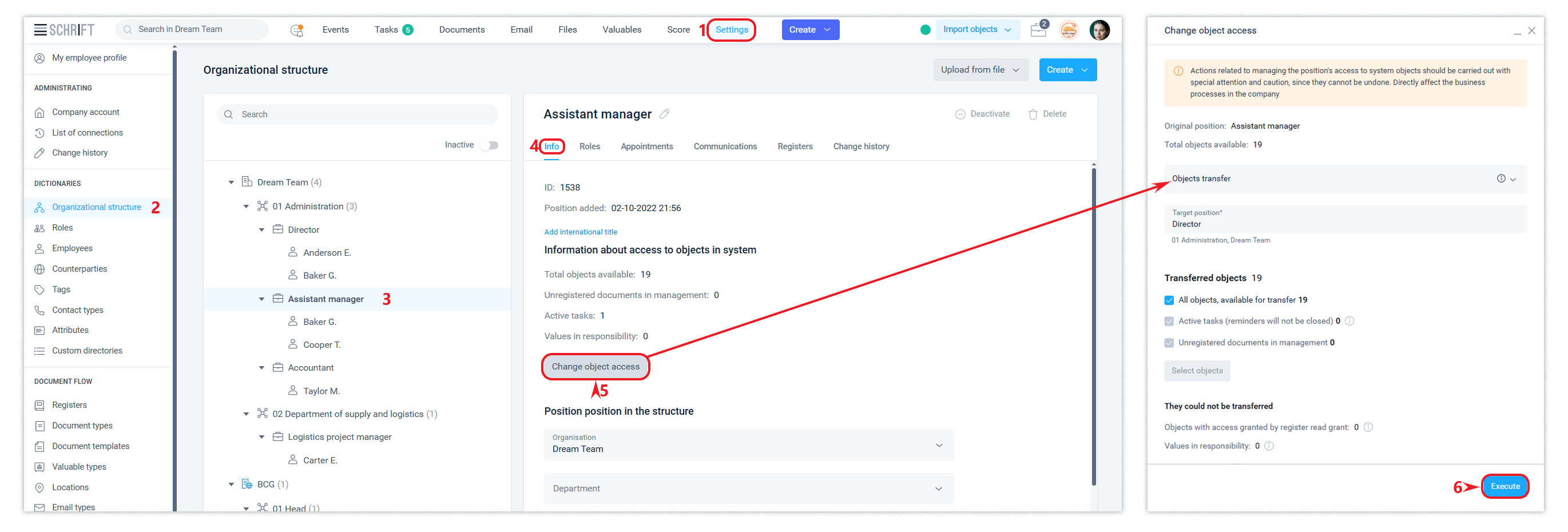
Such actions are usually performed when reorganizing or liquidating a position.
Transferring objects opens access for the recipient position to the objects and all events that were available to the previous position, and at the same time closes access to such objects and all events related to them for the previous position.
After the object is transferred, the recipient position will be displayed in the information about the workgroup and in all other places of the interface instead of the previous position. However, the events and signature and distribution data of the object retain the historical information (at the time of creating the events), which will contain information about the participants of the events who actually performed them in the past period.
When transferring documents and tasks that have not yet been registered and are in the In progress status, in which the source position is responsible, the responsible person changes from the source position to the target position.
The child tasks of the selected objects will be automatically included in the transfer and closing of access. Child tasks of the Signature type will be canceled during the transfer process (if the original position is the initiator) or they will be denied signature (if the original position is the signatory).
When using this transfer tool, valuables cannot be transferred to another position. The transfer of valuables that are the responsibility of the source position is performed using standard system tools, i.e. the actions of the source position.
The restrictions on the performance of actions to the position of an employee who has the role of an owner set out in this article, remain relevant for actions to transfer objects.
Identification codes
For an organization in the organizational structure, for an employee, as well as for a counterparty and a counterparty's contact, the system supports the use of the appropriate identification codes of the country of registration of this entity. The system does not require the mandatory use of codes. They are automatically filled in the data of the relevant directories.
You need to select a country to correctly specify the code and then use it in the processes of signing documents, identifying an employee for access to the company, and others.
